Introduction
According to WHO 25% of world population affected by dermatophytes where in India 6.09-27.6% from south & 62.5% (include HP & UK) population from North reported.1 Most of the developed & tropical climate emerging 18.2-23.2% reported from Brazil, T.mentagrophyte 21.6% from Greece, from USA most of the cases (90%)reported of onychomycosis.2 Squalene epoxidase which diverges in all three groups of dermatophytes & responsible for allylamine resistance, become a striking evidence of modification in several pathogenic genes. Consistent use of Systemic antifungals like Triazoles, Allylamines& Polyenes in combination with steroids improved the pathogen resistance slowly & parallelly damaging the host immunity followed by promoting other microbial predators at skin.3, 4, 5, 6, 7
Objective of Study
Aim of current study to co-relate the demographically preoccupied; mycosis species. Current study specifically treatment failure cases to calculate the Epidemiological cut offs (MIC90) against frequently prescribed drugs for current pathogen, their molecular identification, Cladogram of their pathogenic genes to create phylogenetic relation with already available mycosis genera.
Materials and Methods
It was a cross-sectional & experimental study performed at derma OPDs of public hospitals & subsequently at SIST Biomedical lab Chennai. Protocol for study was approved by ethic clearance committee SIST Chennai.(Ref no 210/IRB-IBSEC/SIST 13 oct 2022). Subjects were informed & written consent has been taken before collection.
Exclusion & Inclusion criteria
Samples collected from group of patients with treatment failure & recurrence tinea, Pregnant, lactating females& kids (up to 14 yr.) were excluded from study to follow Helsinki guidelines for medical research.
Sample size & Statistics
Designed by following formula, for minimum sample size 8
Table 0
|
|
n= required sample size |
|
n = z2xp(1-p)/d2 |
z= confidence level at 95% |
|
|
P= prevalence |
|
|
d= margin of error |
Graph 1
Above graphical presentation explaining the no of various communicable derma infections, carrying patients of both gender reach public hospitals explaining their epidemiology at all three altitudes (Pauri, Almora & Pithoragarh) of Uttarakhand.
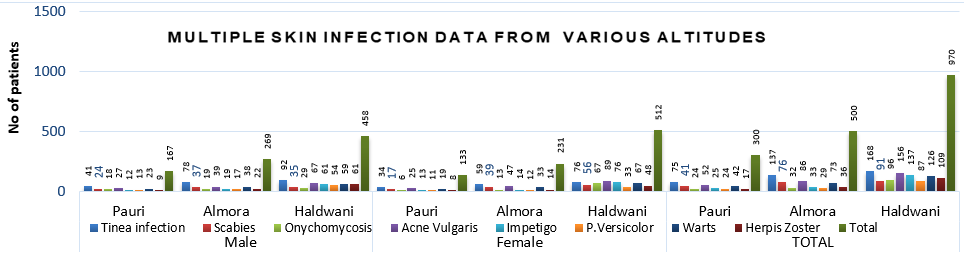
Figure 1
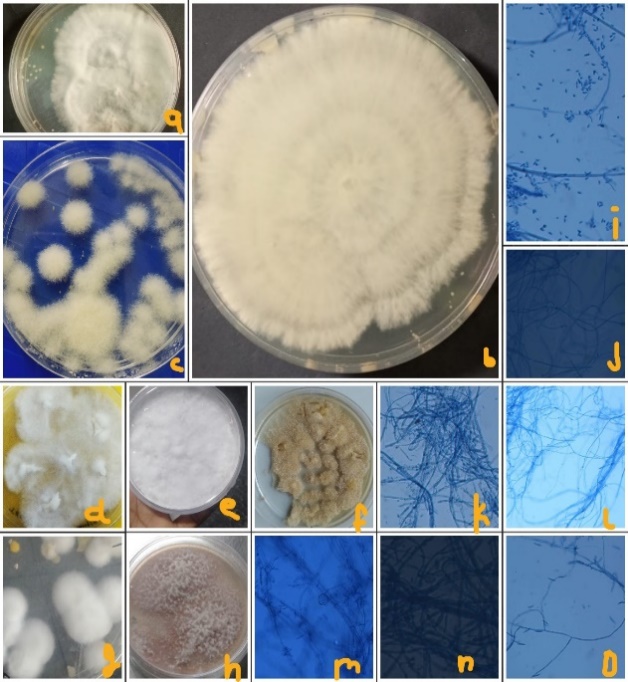
Mycosis collected from various heights of uttarakhand,here T.mentagrophyte (a ,b & m), T.rubrum (d,k-impart red pigment) collected From lower altitude in huge quantity remaining species Epidermophyto(f,j-turns straw colour) microsporum (c,o,h,i), Blastomycis (e,l) collected from higher altitudes in higher quantity.
Graph 2
Above graphica was collected from Pithoragarh, Almora & Pauri patients reach public hospitals of Almora, Haldwani & Pauri, indicating the various mycosis genera isolated from each area.
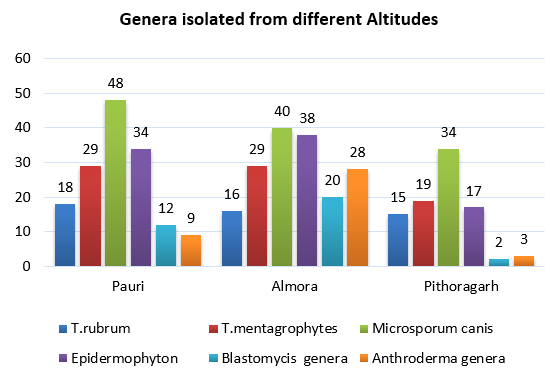
Almost 500,300 & 500 (T-1250 according to population density) patients from Almora, Pauri & pithoragarh were observed subsequently, to target the highest incidences of preoccupied (Figure 1) & reoccurrence pathogen at public hospitals. Which was concluded by putting data in SPSS.After observing data, samples from dead shedding stratum corneum of well-defined margins of tinea; were collected by sterile blunt scalpel,also include infected nails & hair shafts. Concluded quantity of recovered samples was 150,170 & 90 at PDA (from July to Oct 2022, 2023 approx. 30-50 x1 for 3 months) was performed at each location species variation is clearly visible. (Figure 3)
Dermatomycosis culture & identification patterns
Dead marginal stratum corneum collected from patients, preliminary heat fixed with10% KOH & 30% DMSO at slides & observed under trinocular for confirmation of visible filaments. Positive samples, cultured at PDA in sterilized lab conditions. Subsequently replicas were plated in variety of media RPMI 1940, SDA, PDB for genus identification under trinocular stained with lactophenol blue.
White cottony Colonies of culture during monsoon in sterilized lab conditions were visible at 24-280 C in autoclave after 7-9 days. As culture fully grown, color variation due to ample of spores formation in several mycosis genera.In fully grown colonies microconidia, macroconidia & spores visibly effective in genus identification, through tissue culture microscope (TC1000) series, at 10x & 22x power magnification. Hyphae, filaments, conidia including spores shape & size of cottony colonies was helpful during identification (Figure 2).
Clinical break points by CLSI 90 well microdilution experiment
AFST performed by EUCAST method E.def 11.0,9 pure powder of antifungals, dissolved in DMSO to prepare the stock solution (1000mg/ml). Serial 2-fold dilution which is double the final strength solution at RPMI 1640 prepared to calculate the susceptibility range of current pathogen against frequently prescribed antifungals at public hospitals. A fraction of 50µml two-fold dilutions of drug were inoculated by multichannel pipette. A disc diffusion was also performed for which single disc used at one petri plate but 2 discs were also used (for growth study only) for study of a combination of drugs as a preliminary test for pathogenic gene modifications. From middle of disc up to 14 mm was marked as zone of inhibition,15-20mm zone of sensitivity, above 22 mm zone of susceptibility was marked. Results were taken manually thrice for each species along with SD calculation (Table 2 )Drug range for Itraconazole (0.125-0.20µl), Range for fluconazole (0.125-15µl), For terbinafine (0.125-35µl), Almost 0.125-35µl was experimentally designed due to previously available data from similar kind of studies.8 100µg of inoculum (2500-6500 CFU/ml) was added to each well & incubated for a 5-7 days at 280C, readings were taken through turbidity spectrophotometer for accuracy (Table 2). However observation of turbidity clearly visible through reading mirrors also,MIC90 readings were taken (Table 3). Here RPMI 1960 supplemented with cycloheximide 100mg/ml & Chloramphenicol 50mg/ml in ethanol at ph. 7 used as buffering agent . Pure antifungal powdered form was measured by the following formulas. 10
Molecular level identification
Final confirmation of genus identification was done by the ITS regions.11 DNA extraction was performed by kit method (Himedia-MB543) after crushing the fungal colonies with liquid nitrogen.For confirmation of presence of DNA in the extraction buffer SYBR Green was used along with ITS Universal primers 12 (Forward ITS1-5′-TCCGTAGGTGAACCTGCGG-3 ReverseITS4R–5′ -TCCTCCGCTTATTGATATGC- 3′). PCR was carried out (LT-241-96 wells) in 50µl reaction volumes including 25µl of premix,3µl of DNA template,0.8µM of each primer & DDW added to maintain final volume. Reaction mixtures preheated to 980C for 5 min. & then 35 cycles were performed; Initially for 1 min at 960C, then 680C for 1 min & 720C for 1 min. followed by final extension at 720C for 5 minutes. The PCR products with appox.2380bp DNA were purified using a minimum elute PCR purification kit. All amplicons were evaluated at 1.5% agarose gel,loaded with ladder . After confirmation all species samples, subsequently loaded For PCR along with 28s rRNA primers & confirmed by sequencing, which primarily confirmed by the presence of successful copies in SYBR green qPCR master mix. Finally, 28s rRNA (Figure 2) was used to further confirm species. 13
Table 1
[i] Disc diffusion test performed as to find out the breakpoint against antifungals as drugs crosses the zone of Inhibition (0-14mm), Zone of sensitivity (15-20mm) & Zone of susceptibility (22mm & above) .These were the average results of species occupying zones during tests from all three altitudes of Uttarakhand.*pit-Pithoragarh collection *Alm-Almora Collection *Pau-Pauri collection
Table 2
[i] Tabulated data was collected from patients of Almora, Pithoragarh & Pauri region reached public hospitals of Uttarakhand indicating the clinical break points Observed during experiment. Mean was calculated by 5 readings Taken by spectrophotometer, of each species & of each location, then Geometric mean taken as grand mean (Blue).
Squalene epoxidase mutations
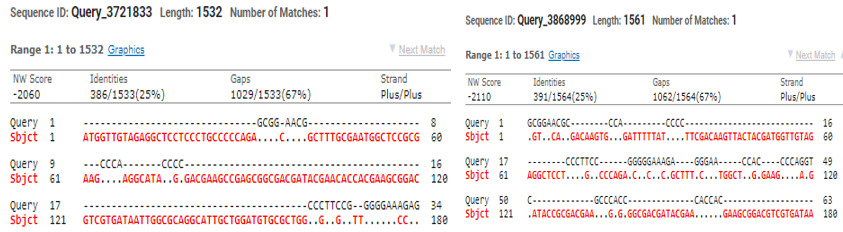
To find out the alterations in SQLE gene, having exceeded MIC readings for terbinafine & other frequently prescribed antifungals were tested by the modified primers where amino acid found modified at Leu 393 Phe, Leu 393 Ser, Phe 397 leu & Gln 408 Leu.Modified primer Drsq1(5ʹ-TTGCCAACGGGGTGTAAAG-3ʹ) & Drsq2(5ʹ-GGGCCATCTATAATTCAGACTC-3ʹ) were used for rRNA multiplication of Tricophyton & Epidermophyton.Length of the SQLE observed was 550bp & 600bp (0ut of 1500bp) subsequently, here two strains with crossing the zone of inhibition to terbinafine was selected to PCR(as above).Both of the sequences of alignment were studied by clustal W pairwise alignment after sequencing. Microsporum, E.flocossum found 15% & T.mentagrophytes (KX906452), T.indotineae (OR862942) found 25% identical when compared with mutated SQLE, however with normal primer Trsq F(5’-ATGGTTGTAGAGGCTCCTCCC-3’) TrsqR(5’-CTAGCTTTGAAGTTCGGCAAA3’) Squalene found 82-92% similar for all the species (Figure 4b).
Epidemiological cut off & Cladogram relatability
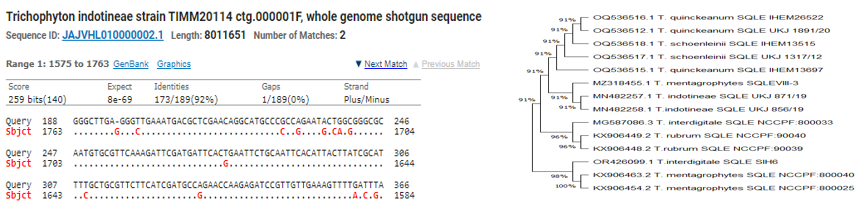
It was noticed that when multiplication performed by Drsq primers & sequencing performed at Barcode Pvt. ltd. Bengaluru by sanger method. A double mutants was observed at F397Leu & Ala448Thr, after sequencing. Not only Sequence alignment but physical appearance also indicating the, T.mentagrophytes colonies with Indotineae. When T.rubrum SQLE (500bp) was sequenced one modification at Leu393Phe was also observed. After multiple sequence alignment of isolated species SQLE comparatively at FASTA NCBI; it was observed closely related & evolving toward T.Indotineae as almost 90% similar mutations were observed.(Figure 4).
Results
Compratively Epidermophyton & Microsporum recovered in huge quantity from higher altitudes. Clinical break points for Trichophyton, Epidermophyton & Microsporum subsequently for terbinafine (11.9-21.6µg/ml), for Itraconazole (0.22-1.25µl/ml) & for Fluconazole (0.12-0.22µl/ml) found much multiplied than previously reported MIC, at all 3 altitudes. SQLE was modified at aa F397L, A448T in mentagrophyte & L393F in rubrum rRNA.
Discussion
Current study includes six dermatophyte genera with 180 Samples, study was divided in two parts; first cross-sectional study, where Disc diffusion tests & microdilution experiments performed for confirmation of MIC50 &MIC90 range for current available pathogens including SQLE multiplicaton & sequencing of two genera. Second part contains multiplication of ITS regions & species identification. Study observes fluconazole MIC90(ranges 0.15-0.69µg/ml) & Itraconazole MIC90(0.058-0.78) was found slightly vary from sharma8 study where itraconazole slightly differ & fluconazole strikingly higher MIC.Here if terbinafine (12.7-11.9µg/ml)results completely contradict. However some studies like sabarter 14 supports current study where terbinafine MIC50 ranges between (0.06-8.0µg/ml) .Griseofulvin resistance 15, 16, 17, 18, 19 was also reported, & supports current study as ranges between 6.24-12.48µl/ml.15 Current study mutations also supported by Bortoluzzi10 found the similar kind of alterations in dermatophyte genotype. So higher ECF or MIC also indicating genotype modifications in dermatophytes. It is difficult to find out the impact of increased MIC directly but associated pharmacokinetics & pharmacodynamics by calculating Cmax/MIC, time of diffusion of drug & AUC/MIC ratios.PK/PD index in serum for increased MIC of antifungals more precisely help to optimize antifungal therapy; such as help to prepare Country/Area specific dosing schedules(i.e OD,BD,TDS,SOS,HS & SOS etc in maximum permissible limit) & accordingly change in combination of drugs with higher impact & low health risk. To override current modified pathogen it is significant to find out their MIC range & PK/PD index (i.e-time of drug infusion in serum & its residing time, to maximize the impact at target organ) guiding practitioners to keep the maximum herd immunity as it is a communicable infection.
In current years from various parts of India 1 & World 11 higher MIC range & related mutations were reported, Frequently higher MIC for terbinafine leads to point mutations; F397L & L393F in T.indotineae, T.rubrum & T.interdigitale. However F415S,H440Y,I121M,V237I point mutations20 were similar for T.rubrum & T.interdigitale. Azole efflux pumps (overexpression of TruMDR2 & Tru MDR3) resulting in azole & terbinafine higher ECF points. As up to 600bp of SQLE were studied during current study so results were similar for point mutations, from Doon valley also but current update from study observed was resistance is more toward higher altitudes.
.
Conclusion
It is difficult to find out the impact of increased MIC directly but helpful in associated pharmacokinetics & pharmacodynamics by calculating Cmax/MIC, time of diffusion of drug & AUC/MIC ratios. PK/PD index in serum for increased MIC of antifungals more precisely to optimize antifungal therapy.