- Visibility 85 Views
- Downloads 9 Downloads
- DOI 10.18231/j.ijced.2021.020
-
CrossMark
- Citation
Evolving eponymous signs in diagnostic dermoscopy
- Author Details:
-
Atul Bothra
-
Seujee Das
-
Anshu Maheswari
-
Mehak Singh
-
Shashank Bhargava *
Introduction
As dermoscopy takes the center stage, numerous dermoscopic features of various dermatological disorders are described. This field of dermatology is very dynamic and still in the evolving phase. Although descriptive terminology is the preferred method for describing dermoscopic lesions, metaphorical terms are widely used, as signs are imaginable, memorable and thus easily identifiable. In this article we attempt to highlight the various dermoscopic signs described in dermatology.
Anal Groove Sign
used to differentiate ixodes ticks from other ticks in Lyme’s disease. In dermoscopy, anal groove is seen as a crescentric depression on the ixodes tick’s ventral surface that wraps anteriorly around the anus while other ticks have it located posteriorly. [1]
Beauty and the beast sign
It refers to the assessment of the overall symmetry of color and form in differentiating benign naevi and melanoma. Beauty refers to those lesions where the dermoscopic appearance is pleasing to the eyes, i.e. there is symmetry in color and form and thus the lesion is not worrisome. In contrast, beast refers to those lesions which lack an overall symmetry of color and form and are thus worrisome. [2] The little red riding hood sign is a similar analogy wherein lesions which look benign from far, on dermoscopy shows subtle features of malignancy.[3]
Blink sign
In hybrid dermoscopes, structures that are more visible with either non-polarized (NPD) or polarized dermoscopy (PD), appear to ‘blink’ when the modes are toggled. In melanoma, chrysalis-like structures are seen with PD which are not seen with NPD and appear to blink, while in seborrheic keratosis, multiple comedo like openings and milia like cysts are more conspicuous with NPD and appear to blink. This is referred to as the Blink sign in dermoscopy. [4]
Blue pseudoveil sign
Seen in dermoscopy of macrocomedones. Macrocomedones contain oxidized keratin plug which on dermoscopy reveals brown or black, homogenous structures which have a whitish-blue halo or whitish-blue structureless areas, referred to as the blue pseudoveil sign, which needs differentiation from melanoma. [5]
Bolognia sign
Seen in acquired melanocytic nevus with an eccentric area of hyperpigmentation (small dark dots) seen on one side, which is named as the ‘Bolognia sign’ and may simulate melanoma. [6]
Bonbon Toffee sign
Sebaceous hyperplasia may show central umbilication surrounded by aggregated white-yellowish globules which is named as the ‘Bonbon toffee sign’ due to its resemblance to the bonbon toffee. [7]
Burnt matchstick sign
Sseen in trichotillomania, implies that the proximal end of hair shaft becoming dark and bulbous resembling a burnt match stick ([Figure 1]). [8]

Color-transition sign
It is a trichoscopic sign differentiating alopecia areata incognita from telogen effluvium. Due to chronic assault in alopecia areata on the bulbs of the hair follicles, the hair shafts have cornified proximal roots showing color graduation from black to clear between the distal end and the proximal root. [9]
Cumulus Sign
Sebaceous hyperplasia on dermoscopy shows the presence of aggregated white-yellowish globules or structures which is known as the ‘cumulus sign’ ([Figure 2]).[10]
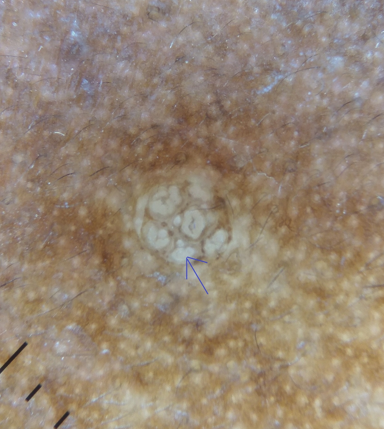
Delta wing jet with contrail sign
Seen in scabies as the triangular or V- shaped structure corresponding to the fore portion of the mite. Also referred to as the ‘triangle sign,’ ‘delta glider,’ ‘delta wing jet,’ ‘jet plane’ or spermatozoid appearance. [11], [12] The presence of the burrow with the mite at its end has been called the ‘jet with contrail’ appearance or the ‘jetliner with its trail’ ([Figure 3]). [13]
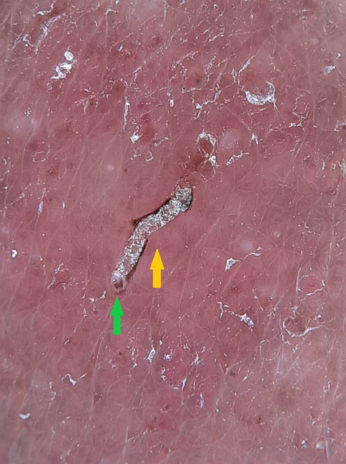
Dermoscopic auspitz sign
Psoriatic lesions on dermoscopy reveals the regular dotted vessels pattern which becomes prominent after removal of the scales. It strengthens the diagnosis of psoriasis, without actually having to induce bleeding and is known as the dermoscopic auspitz sign. It is of particular help in the presence of marked hyperkeratosis which impedes the view of underlying features ([Figure 4]). [14]
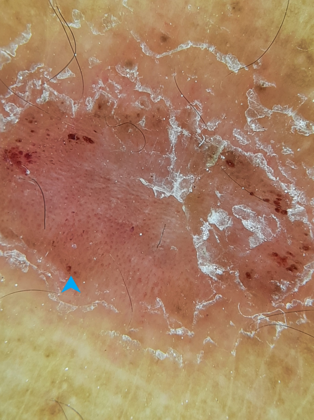
Diamond necklace sign
The dermoscopically diagnostic finding in porokeratosis of Mibelli is the presence of peripheral white border, often double-marginated, corresponding histologically to the cornoid lamella. It has been metaphorically called ‘white track’ or ‘lines of volcanic crater,’ and ‘diamond necklace’([Figure 5]). [15]
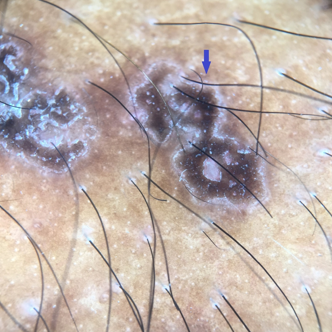
Double edge sign
In Bowen’s disease, the periphery of the lesion on the dermoscope reveals two parallel pigmented edges in 30% cases corresponding histologically to two strips of hyperpigmented basal keratinocytes separated by hypopigmented acanthosis.[16]
Eastern Pancake sign
Alopecic and aseptic nodules of the scalp (AANS) is a rare entity, consisting of a few dome-shaped, skin-colored nodules associated with non-scarring alopecia. Trichoscopy depicts the presence of heterogeneously dilated follicular orifices known as the ‘eastern pancake sign’ along with comedo like openings. [17]
Flambeau sign
Traction alopecia on trichoscopy reveals multiple linear white tracks in the direction of hair pull, at the base of the hair shaft in the area posterior to the fringe over the scalp. These linear tracks in continuation with the hair give an appearance of a flame or lit torch, named the ‘Flambeau sign’. [18]
Fried Egg sign
Seen in trichoscopy of scalp pemphigus, demonstrating multiple yellowish dots with a whitish halo which is believed to correspond to the detached epidermis covering the follicular ostia. [19]
Golf club set sign
Seen in Bullous Aplasia Cutis Congenita (BACC) or membranous Aplasia Cutis. BACC is a specific Subtype of Aplasia Cutis Congenita covered with a membranous surface. Clinically, once the bulla resorbs, it appears as a flat scar with a well-delimitated border and the hair distributed in a rather peculiar collar-like way. Dermoscopy shows, under the translucent membrane, the presence of hair bulbs arranged radially along hair bearing margin, resembling a golf club set. [20]
Handle bar sign
Pseudofolliculitis of the beard area on dermoscopy shows curved hair attached to the skin on both sides, which is referred to as the ‘handle bar’ sign. [21]
Hypopyon sign
Seen in cutaneous angiosarcoma and lymphangioma circumscriptum. Polarised dermoscopy of the lesions shows many clods surrounded by white septa; these clods had three distinct colours: yellow-orange colour, red-purple colour and yellow to orange colour at the superior part and purple-red at the base, referred to as the ‘hypopyon sign’ ([Figure 6]). [22]
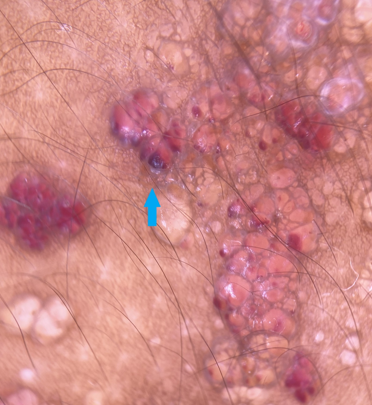
Iceberg sign
Actinic keratoses neglecta on dermoscopy shows a bright arctic-blue keratotic plug resembling an iceberg, known as the ‘iceberg sign’. [23]
Isobar sign
Seen in Lentigo maligna where dermoscopy reveals concentric pigmented circles surrounding follicular openings, known as the circle within a circle sign or Isobar sign. [24]
Jelly sign
Dermoscopic examination of melasma reveals diffuse reticular pigmentation in various shades of brown,sparing the hair follicles and eccrine gland openings and producing an exaggerated pseudo network pattern with concave borders, which mimicks the border of a jelly and is thus called the ‘jelly sign’ ([Figure 7]). [25]
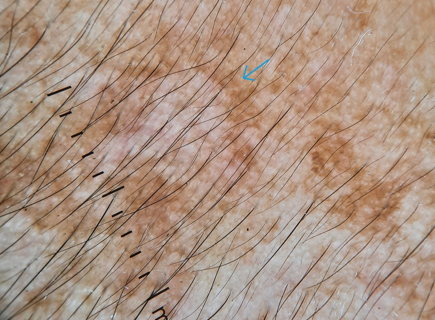
Lightening sign
Used in acral dermoscopy to differentiate hemorrhagic lesions from melanocytic lesions. The trauma induced darkening of skin on pressure points on dermoscopy shows the presence of parallel ridged discolouration and cracks of blood similar to bolts of lightning. [26]
Mace sign
It is described in trichotillomania differentiating it from alopecia areata, where due to the constant pulling action of hair, the distal end of the shaft becomes rough and bulbous in texture resembling a mace([Figure 8]). [27]
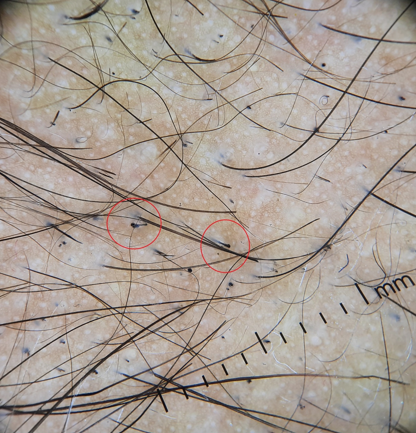
Micro Hutchinson’s sign
Hutchinson sign was described as the periungual extension of the pigment from the nail bed and matrix into the proximal nail fold seen in subungual melanoma differentiating it from other benign conditions. Micro Hutchinson’s sign is it dermoscopic counterpart where very subtle pigmentation of the cuticle or submatrix, not visible to the naked eye can be seen with dermoscopy. [28]
Mistletoe sign
It is described in melanoma in situ and inflammatory junctional melanocytic nevus. It is an alert symptom of abnormal melanocytic proliferation seen as multiple, well circumscribed areas, consisting of non-uniform, at times pseudo-dichotomously branched structures, resembling pseudopods.[29]
Mushroom cloud sign
Seen in melanoma. The ‘mushroom cloud’ represents the hyperpigmented area that has extended in one direction beyond the border of the lesion, and the plume underneath represents the stalk-like projection. This term also combines features of melanoma specifically, asymmetry, irregular border, and multiple colors. [30]
Peripilar sign
Perifollicular brownish halo in trichoscopy of early androgenetic alopecia is regarded as the ‘peripilar sign’ and is suggestive of perifollicular lymphocytic infiltrate ([Figure 9]).[31]
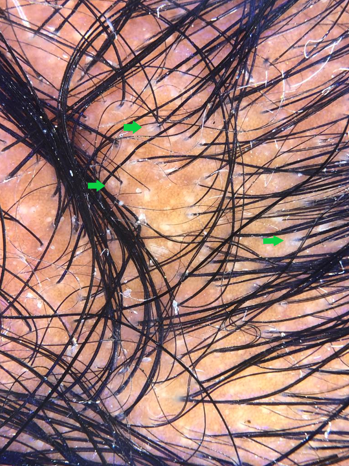
Pink glow sign
Seen in ultraviolet light dermoscopy of glomus tumour. Glomus tumor reveals discrete linear vascular structure on nail plate and numerous ramified telangiectasia on nail bed and matrix during surgery while UV light reveals a pink glow and hence known as the pink glow sign. [32], [33]
Pink rim sign
In melanoma suggests that the presence of a pink rim in the periphery of a melanocytic lesion on dermoscopy is an indicator of malignancy. [34]
Pluck out sign
Dermoscopy reveals round hemorrhages around the hair shafts that could be called the ‘pluck out sign’ which is described in beard trichotillomania to differentiate it from alopecia areata and can be seen in scalp trichotillomania as well. [35]
Poppyfield bleeding sign
Seen in cutaneous malignant melanoma, where squirts of numerous ruby droplets of blood appear on pressing the dermoscope firmly against the lesion. It is a dermoscopic clue to dilated blood vessels and histological ulceration. [36]
Pore sign
Corresponds to the central crater and follicular opening characteristically seen in epidermal cyst. The area where the pore sign appears is filled with keratin and it can be of white, yellow, brown or black colour([Figure 10]). Dermoscopy also helps to differentiate ruptured from unruptured cyst. In the former Peripheral erythema with linear vessels and ivory white color is seen while branching vessels with bluish areas in the centre indicate an unruptured cyst.[37], [38]
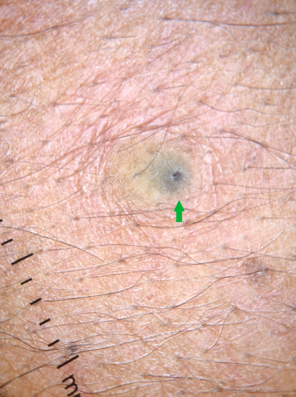
Radial crown sign
Seen in Tungiasis, caused by flea Tunga penetrans. Dermoscopy reveals a black central area with a pore corresponding to the genital opening of the flea with a pigmented peripheral ring corresponding to the posterior abdomen. A radial crown sign is described between the pore and the peripheral ring and corresponds to the zone of columnar hemorrhagic parakeratosis in a radial arrangement. [39], [40]
Rainbow sign
Polarised dermoscopy of nodular Basal cell carcinoma, reveals whitish structureless areas ,whitish crystalline structures and multi-coloredstructureless areas called as ‘rainbow sign’. [41]
Red planet sign
Dermoscopy of superficial angiomyxoma demonstrates a red to maroon, globular, translucent, myxoid exophytic lesion with a delicate vascular lattice network which is reminiscent of telescopic images of the blood moon during lunar eclipses and is termed as the ‘red planet sign’. [42]
Regularly bended ribbon sign
Trichoscopy of monilethrix shows hair shafts with uniform elliptical nodes and intermittent constrictions with hairs that are bended regularly at multiple locations with a tendency to fracture at constriction sites. It is known as ‘regularly bended ribbon sign’ differentiating it from pseudo monilethrix ([Figure 11]).[43]

Ring scales sign
Sseen in polymorphic light eruption where dermoscopy reveals white-colored circular scales which are continuous, arranged in a ring-shaped manner with central clearing against an ochre to light brown background ([Figure 12]). These correspond histopathologically to the scale crust seen atop the stratum corneum. [44]
Rosette sign
Dermoscopy of actinic keratosis shows a rosette sign, characterized by four white pointsarranged as a four-leaf clover inside the follicular openings. However, it is not specific and might be seen in a variety of disorders. [45]
Sagrada Familia sign, digitations and mirror sign
Seen in intraoperative dermoscopy of onychomatricoma. Multiple, regularly spaced and arranged, hyperbolic cavities in the ventral aspect of the nail is termed as ‘Sagrada Familia (SF) sign’ acknowledging the basilica in Barcelona. ‘Mirror sign’ refers to the symmetry of the lesions in the proximal nail fold with finger-like digitations within the tumour being mirrored by the crypts within the nail plate. [46]
Setting sun sign
Seen in Juvenile Xanthogranuloma where dermoscopy reveals an orange yellow background with an erythematous margin and linear branchedvessels, called as the setting sun sign. [47] Although a similar pattern may be observed in spitz nevus, sebaceous hyperplasia, xanthomatousdermatofibroma, histiocytic sarcoma, and mastocytoma on dermoscopy. [48]
Starry night sky sign
Ultraviolet light enhanced trichoscopy of Frontal fibrosing alopecia reveals fluorescence due to the presence of follicular Propionibacterium ,which is reminiscent of ‘starry night over the Rhone’ by Van Gogh, thus called as ‘starry night sky sign’. It indicates the preservation of follicular unit viability and hence a better prognosis. [49]
String of pearls sign
The coiled and dotted vessels in a serpiginous arrangement or ‘string of pearls’ is considered a pathognomic vascular pattern associated with clear cell acanthoma. However, lichen planus like keratoses and seborrheickeratoses have been reported with similar findings. [50]
St.Tropez sign
Initially described for seborrheic keratosis, but can also be seen in dermal naevus, actinic keratoses and porokeratosis. Seen when topical tanning products are used in and the pigment gradually accumulates in the skin surface which on dermoscopy reveals a bizarre pigmentation referred to as the St.Tropez sign. [51]
Translucency sign
Dermoscopy of membranous aplasia cutis congenital shows a reddish background with thin, linear vessels and few hair bulbs seen by the translucency of the lesion known as the ‘translucency sign’. [52]
Triangular sign
The triangular sign in nail melanonychia indicates gradual enlargement of pigment bands in which the proximal part is broader than the distal portion and is found in 5% to 25% of nail unit melanomas. However, studies have mentioned the presence of triangular sign in nail matrix naevi. [53]
V sign
V sign is seen in trichotillomania when two or more hairs emerging from a single follicular ostia are pulled simultaneously and break at similar length above the surface resembling the alphabet V, known as the ‘V- sign’. [54]
Wobble sign
Seen in benign elevated melanocytic nevus.The melanocytic nevus has a papillomatous central part with exophytic papillary structures. When the dermoscope is pushed horizontally, parallel to the surface, the most elevated part of the lesion sticks to the scope and the papillomatous nevus is seen as moving: this is known as the wobble sign. It can also be used to differentiate it from seborrheic keratosis. [55]
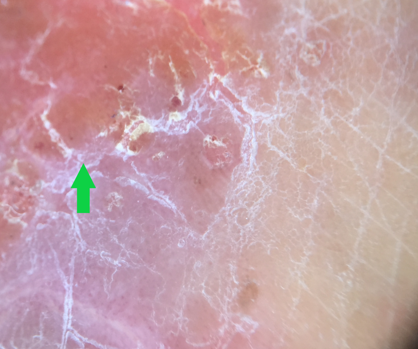
Yellow clod sign
Seen in nummular eczema, where serum exudates are seen as yellow clods with a diameter of 1 to 2 mm (Figure 13) differentiating it from psoriasis and dermatophytosis. These yellow clods are better seen with immersion fluid.[56]
Source of Funding
No financial support was received for the work within this manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
There are no conflicts of interest.
References
- DM Connolly, JB Lee. The anal groove sign: The use of dermatoscopy for identification of Ixodes ticks. J Am Acad Dermatol 2017. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- A A Marghoob, A J Korzenko, L Changchien, A Scope, R P Braun, H Rabinovitz. The beauty and the beast sign in dermoscopy. Dermatol Surg 2007. [Google Scholar]
- JM Mascaro. The Dermatologist's Position Concerning Nevi: A Vision Ranging From "The Ugly Duckling" to "Little Red Riding Hood". Arch Dermatol 1998. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- RP Braun, A Scope, AA Marghoob. The "Blink Sign" in Dermoscopy. Arch Dermatol 2011. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- G Kaminska-Winciorek. Blue Pseudo-Veil Sign”-a New Dermoscopic Term?. Dermatol Surg 2012. [Google Scholar]
- MA Pizzichetta, C Massone, G Grandi, G Pelizzo, HP Soyer. Morphologic Changes of Acquired Melanocytic Nevi With Eccentric Foci of Hyperpigmentation (“Bolognia Sign”) Assessed by Dermoscopy. Arch Dermatol 2006. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- P Oztas, M Polat, M Oztas, N Alli, H Ustun. Bonbon toffee sign: a new dermatoscopic feature for sebaceous hyperplasia. J Eur Academy Dermatol Venereol 2008. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- SMukherjee, S Malakar. Burnt matchstick sign - A new trichoscopic finding in trichotillomania. Int J Trichology 2017. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- M Kinoshita-Ise, M Fukuyama, M Ohyama. Color-transition sign: A useful trichoscopic finding for differentiating alopecia areata incognita from telogen effluvium. J Dermatol 2018. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- AM Bryden, RS Dawe, C Fleming. Dermatoscopic features of benign sebaceous proliferation. Clin Exp Dermatol 2004. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- C. Prins, L. Stucki, L. French, JH Saurat, RP Braun. Dermoscopy for the in vivo Detection of Sarcoptes scabiei. Dermatology 2004. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- J H Park, C W Kim, S S Kim. The diagnostic accuracy of dermoscopy for scabies. Ann Dermatol 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Deepak Jakhar, Chander Grover. Dermoscopy in the Diagnosis of Scabies. Int J Dermoscopy 2017. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- F Kaliyadan. The dermoscopic auspitz sign. Indian Dermatol Online J 2018. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- MA Pizzichetta, V Canzonieri, C Massone, HP Soyer. Clinical and Dermoscopic Features of Porokeratosis of Mibelli. Arch Dermatol 2009. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Y Yang, J Lin, S Fang, S Han, Z Song. What's new in dermoscopy of Bowen's disease: two new dermoscopic signs and its differential diagnosis. Int J Dermatol 2017. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Y Bourezane, H Bourezane. Two new trichoscopic signs in alopecic and aseptic nodules of the scalp: “Eastern pancake sign” and comedo-like structures. Ann Dermatol Venereol 2014. [Google Scholar]
- S Agrawal, SB Daruwalla, RS Dhurat. The flambeau sign – A new dermoscopy finding in a case of marginal traction alopecia. Australas J Dermatol 2020. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- M. Ghiasi, M. Nasimi, A. Ghanadan, S. Azizzadeh‐Roodpishi. ‘Fried Egg Sign’: A trichoscopic feature in scalp pemphigus. Journal of the European Academy of Dermatology and Venereology 2020. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- M Cutrone, R Grimalt. The Trichoscopic “Golf Club Set” Sign for Bullous Aplasia Cutis Congenita. Skin Appendage Disord 2018. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- F Kaliyadan, J Kuruvilla, HYA Ojail, SA Quadri. Clinical and dermoscopic study of pseudofolliculitis of the beard area. Int J Trichol 2016. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- S Bostancı, BN Akay, S Vural, P Ertop, AO Heper. Hypopyon sign in dermatoscopy of cutaneous angiosarcoma. Australas J Dermatol 2019. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- J.F. Mir‐Bonafé, E. Rozas‐Muñoz, J. Dalmau, M. Mir‐Bonafé, H. Iznardo, C. García‐Melendo. Iceberg sign as a dermoscopic clue of actinic keratosis neglecta. J Eur Academy Dermatol Venereol 2019. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- N Jaimes, AA Marghoob, H Rabinovitz, RP Braun, A Cameron, C Rosendahl. Clinical and dermoscopic characteristics of melanomas on nonfacial chronically sun-damaged skin. J Am Acad Dermatol 2015. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Manjunath K. G., Kiran C., Sonakshi S., Ritu Agrawal. Melasma: Through the eye of a dermoscope. Int J Res Dermatol 2016. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- Helen Audrain, David DeBerker. “Lightening sign” in acral dermoscopy. BMJ 2016. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- S Malakar, SS Mukherjee. ‘Mace sign’- A definitive sign of trichotillomania?. Our Dermatol Online 2017. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- E. Benati, S. Ribero, C. Longo, S. Piana, S. Puig, C. Carrera. Clinical and dermoscopic clues to differentiate pigmented nail bands: an International Dermoscopy Society study. J Eur Acad Dermatol Venereol 2017. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- G Kamińska-Winciorek, P Właszczuk, Jerzy Wydmański. “Mistletoe sign”: probably a new dermoscopic descriptor for melanoma in situ and melanocytic junctional nevus in the inflammatory stage. Adv Dermatol Allergol 2013. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- MJ Mahlberg, C Hwa, AW Kopf, JA Stein. Letter: “Mushroom-Cloud Sign” of Melanoma. Dermatol Surg 2011. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- C Deloche, O Lacharrière, C Misciali, BM Piraccini, C Vincenzi, P Bastien. Histological features of peripilar signs associated with androgenetic alopecia. Arch Dermatol Res 2004. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- S L Maehara, E M Ohe, M Y Enokihara, N S Michalany, S Yamada, S H Hirata. Diagnosis of glomustumor by nail bed and nail matrix dermoscopy. An Bras Dermatol 2010. [Google Scholar]
- SS Thatte, SB Chikhalkar, US Khopkar. "Pink glow": A new sign for the diagnosis of glomus tumor on ultraviolet light dermoscopy. Indian Dermatol Online J 2015. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- RK Rader, KS Payne, U Guntupalli, HS Rabinovitz, MC Oliviero, RJ Drugge. The Pink Rim Sign: Location of Pink as an Indicator of Melanoma in Dermoscopic Images. J Skin Cancer 2014. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- M Cutrone, R Grimalt. The Dermoscopic “Pluck Out Sign” for Beard Trichotillomania. Skin Appendage Disord 2018. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- HF Lorentzen, K Weismann, K Rossen, HK Thomsen. Poppyfield Bleeding: a New Dermatoscopic Sign and its Histopathological Background. Acta Dermato-Venereol 2007. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- G. Ghigliotti, E. Cinotti, A. Parodi. Usefulness of dermoscopy for the diagnosis of epidermal cyst: the ‘pore’ sign. Clin Exp Dermatol 2014. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- K S Suh, D Y Kang, J B Park, M H Yang, J H Kim, K H Lee. Usefulness of dermoscopy in the differential diagnosis of ruptured and unruptured epidermal cysts. Ann Dermatol 2017. [Google Scholar]
- G Marazza, A Campanelli, G Kaya, RP Braun, JH Saurat, V Piguet. Tunga penetrans: Description of a New Dermoscopic Sign—The Radial Crown. Arch Dermatol 2009. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- K Cataldo, S Alvarez, A Abarzua. Dermoscopy in tungiasis. Indian J Dermatol, Venereol, Leprol 2014. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- B Nirmal, AS Krishnaram, R Sudhagar. Rainbow sign in dermatoscopy of nodular basal cell carcinoma. Indian J Dermatopathol Diagn Dermatol 2019. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- M Green, N Logemann, D J Sulit. Myxoidstroma and delicate vasculature of a superficial angiomyxoma give rise to the red planet sign. Dermatol Online J 2004. [Google Scholar]
- A Rakowska, M Slowinska, J Czuwara, M Olszewska, L Rudnicka. Dermoscopy as a tool for rapid diagnosis of monilethrix. J Drugs Dermatol 2007. [Google Scholar]
- S Malakar, P Mehta. Ring Scales: A New Dermoscopic Sign in Polymorphous Light Eruption. Int J Dermoscopy 2017. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- J H Lee, C Y Won, G M Kim, S Y Kim. Dermoscopic features of actinic keratosis and follow up with dermoscopy: a pilot study. J Dermatol 2014. [Google Scholar]
- E. Ginoux, M. Perier Muzet, N. Poulalhon, S. Debarbieux, S. Dalle, L. Thomas. Intraoperative dermoscopic features of onychomatricoma: a review of 10 cases. Clin Exp Dermatol 2017. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- A Palmer, J Bowling. Dermoscopic Appearance of Juvenile Xanthogranuloma. Dermatol 2007. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- N Litaiem, F Zeglaoui. Is the setting sun dermoscopic pattern specific to juvenile xanthogranuloma?. J Am Acad Dermatol 2018. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- ARR Barata, OM Arrones, DS Corralo, SV Galvan. The “Starry night sky sign” Using ultraviolet-light-enhanced trichoscopy: A new sign that may predict efficacy of treatment in frontal fibrosing alopecia. Int J Trichol 2018. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- AE Domínguez Espinosa, BN Akay, RA González-Ramírez. “String of pearls pattern”: report of three cases of non clear-cell acanthoma. An Bras Dermatol 2017. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- SD Orpin, PW Preston, A Salim. The 'St. Tropez' sign; a new dermoscopic feature of seborrhoeic keratoses?. Clin Exp Dermatol 2006. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- B Lozano-Masdemont. A case of membranous aplasia cutis congenita and dermoscopic features. Int J Trichol 2017. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- J Ohn, YS Choe, M Je-Ho. Dermoscopic features of nail matrix nevus (NMN) in adults and children: A comparative analysis. J Am Acad Dermatol 2016. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- A Rakowska, M Slowinska, M Olszewska, L Rudnicka. New Trichoscopy Findings in Trichotillomania: Flame Hairs, V-sign, Hook Hairs, Hair Powder, Tulip Hairs. Acta Dermato Venereol 2014. [Google Scholar] [Crossref]
- R P Braun, J Krischer, J H Saurat. The Wobble Sign in Epiluminescence Microscopy as a Novel Clue to the Differential Diagnosis of Pigmented Skin Lesions. Arch Dermatol 2000. [Google Scholar]
- A A Navarini, L Feldmeyer, P Fritsche, J Kamarashev, L E French, R P Braun. The yellow clod sign. Arch Dermatol 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Introduction
- Anal Groove Sign
- Beauty and the beast sign
- Blink sign
- Blue pseudoveil sign
- Bolognia sign
- Bonbon Toffee sign
- Burnt matchstick sign
- Color-transition sign
- Cumulus Sign
- Delta wing jet with contrail sign
- Dermoscopic auspitz sign
- Diamond necklace sign
- Double edge sign
- Eastern Pancake sign
- Flambeau sign
- Fried Egg sign
- Golf club set sign
- Handle bar sign
- Hypopyon sign
- Iceberg sign
- Isobar sign
- Jelly sign
- Lightening sign
- Mace sign
- Micro Hutchinson’s sign
- Mistletoe sign
- Mushroom cloud sign
- Peripilar sign
- Pink glow sign
- Pink rim sign
- Pluck out sign
- Poppyfield bleeding sign
- Pore sign
- Radial crown sign
- Rainbow sign
- Red planet sign
- Regularly bended ribbon sign
- Ring scales sign
- Rosette sign
- Sagrada Familia sign, digitations and mirror sign
- Setting sun sign
- Starry night sky sign
- String of pearls sign
- St.Tropez sign
- Translucency sign
- Triangular sign
- V sign
- Wobble sign
- Yellow clod sign
- Source of Funding
- Conflicts of Interest
